Download CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate.200-125.ExamTopics.2026-01-27.59q.tqb
| Vendor: | Cisco |
| Exam Code: | 200-125 |
| Exam Name: | CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate |
| Date: | Jan 27, 2026 |
| File Size: | 4 MB |
How to open TQB files?
Files with TQB (Taurus Question Bank) extension can be opened by Taurus Exam Studio.
Purchase
Coupon: TAURUSSIM_20OFF
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which value is used to determine the active router in an HSRP default configuration?
- Router loopback address
- Router IP address
- Router priority
- Router tracking number
Correct answer: B
Question 2
How many bits are contained in each field of an IPv6 address?
- 24
- 4
- 8
- 16
Correct answer: D
Question 3
Which two circumstances can cause collision domain issues on VLAN domain? (Choose two.)
- duplex mismatches on Ethernet segments in the same VLAN
- multiple errors on switchport interfaces
- congestion on the switch inband path
- a failing NIC in an end device
- an overloaded shared segment
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
Collision Domains -A collision domain is an area of a single LAN where end stations contend for access to the network because all end stations are connected to a shared physical medium. If two connected devices transmit onto the media at the same time, a collision occurs. When a collision occurs, a JAM signal is sent on the network, indicating that a collision has occurred and that devices should ignore any fragmented data associated with the collision. Both sending devices back off sending their data for a random amount and then try again if the medium is free for transmission. Therefore, collisions effectively delay transmission of data, lowering the effective throughput available to a device. The more devices that are attached to a collision domain, the greater the chances of collisions; this results in lower bandwidth and performance for each device attached to the collision domain. Bridges and switches terminate the physical signal path of a collision domain, allowing you to segment separate collision domains, breaking them up into multiple smaller pieces to provide more bandwidth per user within the new collision domains formed. Collision Domains -
A collision domain is an area of a single LAN where end stations contend for access to the network because all end stations are connected to a shared physical medium. If two connected devices transmit onto the media at the same time, a collision occurs. When a collision occurs, a JAM signal is sent on the network, indicating that a collision has occurred and that devices should ignore any fragmented data associated with the collision. Both sending devices back off sending their data for a random amount and then try again if the medium is free for transmission. Therefore, collisions effectively delay transmission of data, lowering the effective throughput available to a device. The more devices that are attached to a collision domain, the greater the chances of collisions; this results in lower bandwidth and performance for each device attached to the collision domain. Bridges and switches terminate the physical signal path of a collision domain, allowing you to segment separate collision domains, breaking them up into multiple smaller pieces to provide more bandwidth per user within the new collision domains formed.
Question 4
Instructions -
This item contains several questions that you must answer. You can view these questions by clicking on the corresponding button to the left. Changing questions can be accomplished by clicking the numbers to the left question. In order to complete the questions, you will need to refer to the topology.
To gain access to the topology, click on the topology button of the screen. When you have finished viewing the topology, you can return to your questions by clicking on the Questions button to the left.
Each of the windows can be minimized by clicking on the [-]. You can also reposition a window by dragging it by the title bar.
Scenario -
Refer to the topology. The diagram represents a small network with a single connection to the Internet.
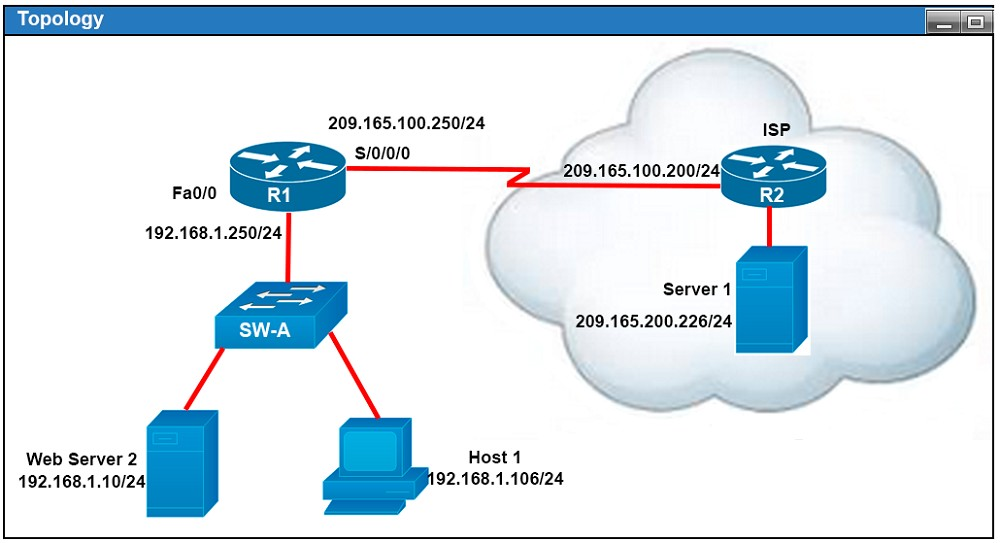
If the router R1 has a packet with a destination address 192.168.1.255, what describes the operation of the network?
- R1 will forward the packet out all interfaces.
- R1 will drop this packet because this it is not a valid IP address.
- As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will add 192.168.1.255 to its MAC table.
- R1 will encapsulate the packet in a frame with a destination MAC address of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.
- As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will forward it to the device assigned the IP address of 192.168.1.255. B
Correct answer: Explanation
Question 5
What is the authoritative source for an address lookup?
- a recursive DNS search
- the operating system cache
- the ISP local cache
- the browser cache
Correct answer: A
Question 6
Scenario -
Refer to the topology. Your company has decided to connect the main office with three other remote branch offices using point-to-point serial links.
You are required to troubleshoot and resolve OSPF neighbor adjacency issues between the main office and the routers located in the remote branch offices.
Use appropriate show commands to troubleshoot the issues and answer all four questions.
Instructions -
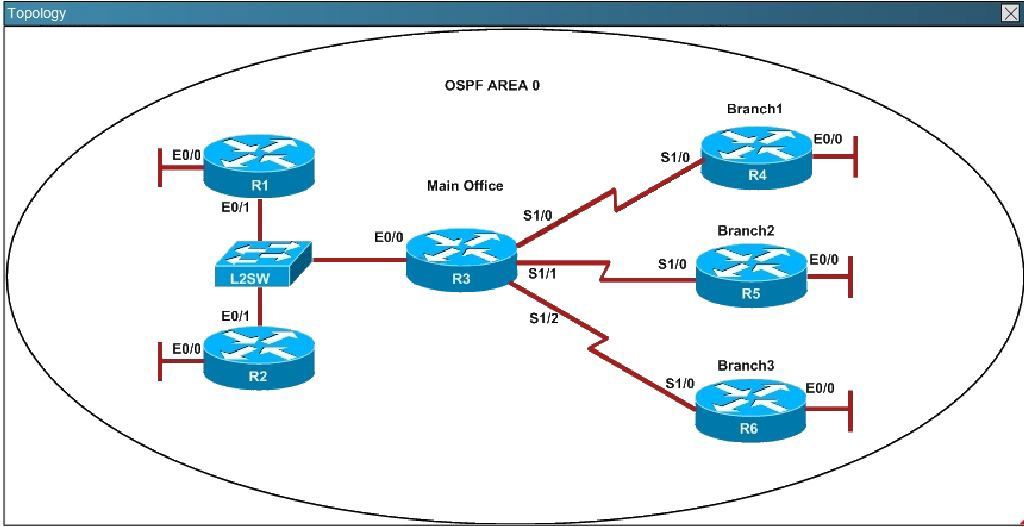


An OSPF neighbor adjacency is not formed between R3 in the main office and R6 in the Branch3 office. What is causing the problem?
- There is an area ID mismatch.
- There is a PPP authentication issue; the username is not configured on R3 and R6.
- There is an OSPF hello and dead interval mismatch.
- The R3 router ID is configured on R6. D
Correct answer: Explanation
Explanation:
Here are the relevant parts of the router configs: We are not sure about the configuration of ppp authentication in this case. Some reports said that only one router has the "ppp authentication chap" command but it is just a trick and is not the problem here. The real problem here is R6 uses the same router-id of R3 (192.168.3.3) so OSPF neighborship cannot be established. In real life, such configuration error will be shown in the command line interface (CLI). So please check carefully for this question. Here are the relevant parts of the router configs:

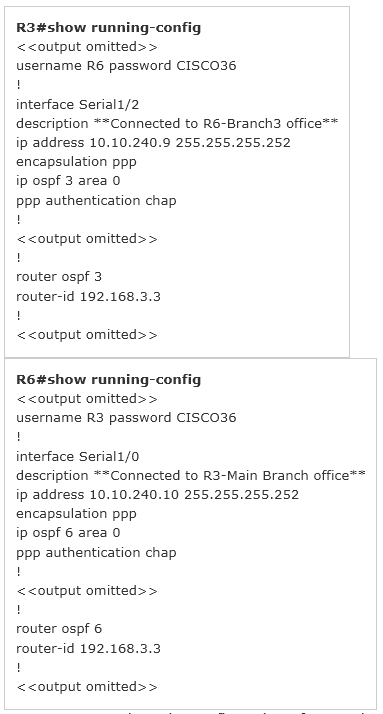
We are not sure about the configuration of ppp authentication in this case. Some reports said that only one router has the "ppp authentication chap" command but it is just a trick and is not the problem here. The real problem here is R6 uses the same router-id of R3 (192.168.3.3) so OSPF neighborship cannot be established. In real life, such configuration error will be shown in the command line interface (CLI). So please check carefully for this question.
Question 7
The output of the show frame-relay pvc command shows "PVC STATUS=INACTIVE". What does this mean?
- The PVC is configured correctly and is operating normally, but no data packets have been detected for more than five minutes.
- The PVC is configured correctly, is operating normally, and is no longer actively seeking the address the remote route.
- The PVC is configured correctly, is operating normally, and is waiting for interesting to trigger a call to the remote router.
- The PVC is configured correctly on the local switch, but there is a problem on the remote end of the PVC.
- The PVC is not configured on the switch.
Correct answer: D
Question 8
Which option is the master redundancy scheme for stacked switches?
- 1:N
- 1:1
- N:1
- 1+N A
Correct answer: Explanation
Question 9
Which protocol does ipv6 use to discover other ipv6 nodes on the same segment?
- CLNS
- TCPv6
- NHRP
- NDP
- ARP
Correct answer: D
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
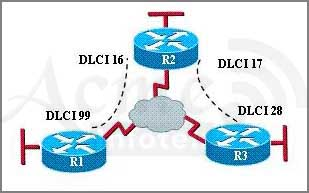
In the Frame Relay network, which IP addresses would be assigned to the interfaces with point-to- point PVCs?
- DLCI 16: 192.168.10.1 /24 DLCI 17: 192.168.10.1 /24 DLCI 99: 192.168.10.2 /24 DLCI 28: 192.168.10.3 /24
- DLCI 16: 192.168.10.1 /24 DLCI 17: 192.168.11.1 /24 DLCI 99: 192.168.12.1 /24 DLCI 28: 192.168.13.1 /24
- DLCI 16: 192.168.10.1 /24 DLCI 17: 192.168.10.2 /24 DLCI 99: 192.168.10.3 /24 DLCI 28: 192.168.10.4 /24
- DLCI 16: 192.168.10.1 /24 DLCI 17: 192.168.11.1 /24 DLCI 99: 192.168.10.2 /24
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
383 383
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!