Download Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist SP (JNCIS-SP).JN0-360.ExamTopics.2026-01-20.76q.vcex
| Vendor: | Juniper |
| Exam Code: | JN0-360 |
| Exam Name: | Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist SP (JNCIS-SP) |
| Date: | Jan 20, 2026 |
| File Size: | 2 MB |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Purchase
Coupon: TAURUSSIM_20OFF
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which two routing-instance types are used for non-VPN-related applications? (Choose two.)
- virtual-router
- vrf
- forwarding
- vpls
Correct answer: AC
Question 2
What are Martian addresses on a Junos device?
- IP addresses that are reserved for use only with MPLS VPNs.
- IP addresses that are never installed in the routing table.
- IP addresses that are reserved for use only with GRE tunnels.
- IP addresses specifically used for out-of-band management.
Correct answer: B
Question 3
Which label operation is performed by an MPLS transit router?
- inject
- pop
- push
- swap
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/software/junos-security/junos-security96/junos-security-swconfig-interfaces-and-routing/mpls-ov.html http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/software/junos-security/junos-security96/junos-security-swconfig-interfaces-and-routing/mpls-ov.html
Question 4
Click the Exhibit button.
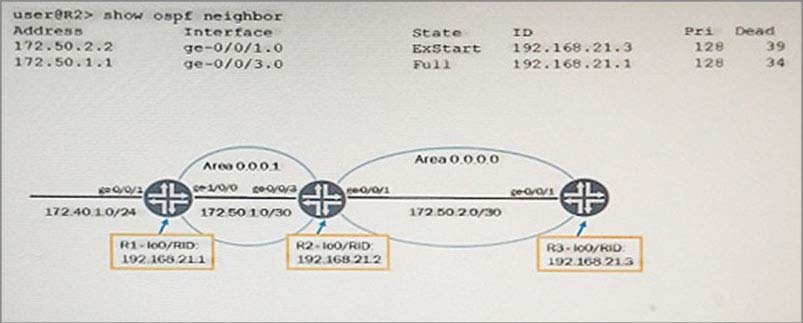
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct about R2? (Choose two.)
- If R2 remains in the ExStart state, then you should verify the MTU setting on R2 and R3.
- R2 LSDB is synchronized with R1.
- If R2 remains in the ExStart state, then you should verify Physical Layer and Data Link Layer connectivity on R2 and R3.
- R2 LSDB is not synchronized with R1.
Correct answer: AB
Question 5
What are three IS-IS PDU types? (Choose three.)
- type length value
- link-state
- partial sequence number
- database description
- complete sequence number
Correct answer: BCE
Question 6
By default, which two tasks does an Ethernet bridge perform in response to receiving a multicast frame? (Choose two.)
- It learns the MAC address of any responding nodes and updates its bridge table with the source MAC address and ingress port
- It drops the frame
- It floods the frame out of all interfaces except the one on which it was received
- It floods the frame out of particular interfaces based on its multicast MAC table.
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
Multicast packets are flooded out all ports except for the port on which it was received. When an unknown destination responds to traffic that has been flooded through a switch, the switch learns the MAC address fo that node and updates its bridge table with the source MAC address and ingress port. Multicast packets are flooded out all ports except for the port on which it was received. When an unknown destination responds to traffic that has been flooded through a switch, the switch learns the MAC address fo that node and updates its bridge table with the source MAC address and ingress port.
Question 7
An Ethernet bridge is configured such that all interfaces are in a single broadcast domain. Which two tasks does an Ethernet bridge perform in response to receiving a frame with an unknown unicast destination MAC address? (Choose two.)
- It drops the frame.
- It floods the frame out of all interfaces except the one on which is was received.
- It learns the destination MAC address when it sees return traffic from the device.
- It learns the source MAC address when it sees return traffic from that device.
Correct answer: BC
Explanation:
When a bridge receives a data frame with an unknown destination MAC address, the frame is flooded out all other ports in the same broadcast domain. Once the bridge sees return traffic from this MAC address, it adds the address to the bridge table. When a bridge receives a data frame with an unknown destination MAC address, the frame is flooded out all other ports in the same broadcast domain. Once the bridge sees return traffic from this MAC address, it adds the address to the bridge table.
Question 8
Using industry best practices, which BGP attribute would you modify to influence how traffic leaves your network?
- MED
- local preference
- AS-path
- communities
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
The BGP local-preference attribute can be used to influence how traffic leaves your network. BGP uses the local-preference attribute only within an AS. Local preference values are not transmitted across EBGP links. The BGP local-preference attribute can be used to influence how traffic leaves your network. BGP uses the local-preference attribute only within an AS. Local preference values are not transmitted across EBGP links.
Question 9
What are three BGP attributes used in the route-selection process? (Choose three.)
- local preference
- communities
- MED
- origin
- atomic aggregate
Correct answer: ACD
Explanation:
When a Junos device receives two similar route advertisements from different BGP peers, it will select the route will the lowest MED value. BGP route selection proceeds in this manner:Prefer the highest local-preference valuePrefer the shortest AS-path lengthPrefer the lowest origin valuePrefer the lowest MED value -Prefer routes learned from an EBGP peer over an IBGP peerPrefer best exit from ASFor EBGP-receive routes, prefer the current active route:otherwise, prefer routes from the peer with the lowest RIDPrefer paths with the shortest cluster lengthPrefer routes from the peer with the lowest peer ID When a Junos device receives two similar route advertisements from different BGP peers, it will select the route will the lowest MED value. BGP route selection proceeds in this manner:
- Prefer the highest local-preference value
- Prefer the shortest AS-path length
- Prefer the lowest origin value
Prefer the lowest MED value -
- Prefer routes learned from an EBGP peer over an IBGP peer
- Prefer best exit from AS
- For EBGP-receive routes, prefer the current active route:
- otherwise, prefer routes from the peer with the lowest RID
- Prefer paths with the shortest cluster length
- Prefer routes from the peer with the lowest peer ID
Question 10
Which two statements are true about the BGP MED attribute? (Choose two.)
- It has a default value of 100
- It has an assumed value of 0
- It is designed for use when multiple connections exist between the same two autonomous systems
- It is designed for use when a BGP router is peering with at least two different autonomous systems
Correct answer: BC
Explanation:
MED is used to help influence the preferred path back into the autonomous system when multiple links exist between the same two autonomous systems. BGP routes do not require the MED attribute. If it is missing, BGP assumes the MED value is 0. MED is used to help influence the preferred path back into the autonomous system when multiple links exist between the same two autonomous systems. BGP routes do not require the MED attribute. If it is missing, BGP assumes the MED value is 0.
Question 11
You are logged in to an MX80 and issue the command "show route protocol bgp" You see that you have received the route 10.0.4/24 from two different peers.
One peer is an external peer and the other is an internal peer. The route received from the internal peer is active.
By the rules of BGP preference, what would cause the internal path for this prefix to be preferred over the external one?
- Internally learned prefix is preferred over an externally learned prefix
- The local-preference value of the internally learned prefix is higher than the externally learned peer
- The peer ID of the internally learned prefix is lower than that of the externally learned peer
- The internally learned prefix has a shorted cluster length
Correct answer: B
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!



